 Personal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to a computer case to create a personal computerupon which system software is installed including a firmware interface such as aBIOS and an operating system supporting application software that performs the operator's desired functions. Operating systems usually communicate with devices through hardware buses by using software device drivers.
Personal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to a computer case to create a personal computerupon which system software is installed including a firmware interface such as aBIOS and an operating system supporting application software that performs the operator's desired functions. Operating systems usually communicate with devices through hardware buses by using software device drivers.Motherboard
The motherboard is the main component inside the case. It is a large rectangular board with integrated circuitry that connects the other parts of the computer including the CPU, the RAM, the disk drives (CD, DVD, hard disk, or any others) as well as any peripherals connected via the ports or theexpansion slots.
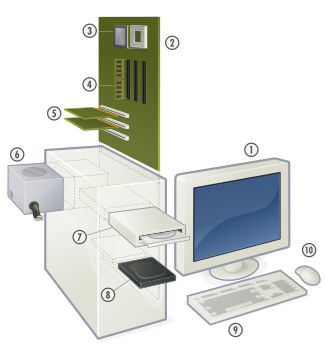
Components directly attached to the motherboard include:Hardware of a modern personal computer
1. Monitor
2. Motherboard
3. CPU
4. RAM
5. Expansion cards
6. Power supply
7. Optical disc drive
8. Hard disk drive
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse
2. Motherboard
3. CPU
4. RAM
5. Expansion cards
6. Power supply
7. Optical disc drive
8. Hard disk drive
9. Keyboard
10. Mouse
- The CPU (Central Processing Unit) performs most of the calculations which enable a computer to function, and is sometimes referred to as the "brain" of the computer. It is usually cooled by a heat sink and fan. Newer CPUs include an on-die Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
- The Chipset mediates communication between the CPU and the other components of the system, including main memory.
- The RAM (Random-access Memory) stores resident part of the current running OS (OS core and so on) and all running processes (application parts, using CPU or input/output (I/O) channels or waiting for CPU or I/O channels).
- The BIOS (Basic Input Output System) includes boot firmware and power management. The tasks are handled by operating systemdrivers. Newer motherboards use Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) instead of BIOS.
- The ROM (Read-only Memory) stores the initial program that runs when the computer is powered on or otherwise begins execution (Bootstrapping also known as "booting" or "booting up"). Usually stores the BIOS or UEFI.
- Internal buses connect the CPU to various internal components and to expansion cards for graphics and sound.
- Current
- The north bridge memory controller, for RAM and PCI Express
- PCI Express, for expansion cards such as graphics, lannd and physics processors, and high-end network interfaces
- PCI, for other expansion cards
- SATA, for disk drives
- ATA
- The north bridge memory controller, for RAM and PCI Express
- Obsolete
- Current
- External bus controllers support ports for external peripherals. These ports may be controlled directly by the south bridge I/O controller or based on expansion cards attached to the motherboard through the PCI bus.
Power supply
A power supply unit (PSU) converts alternating current (AC) electric power to low-voltage DC power for the internal components of the computer. Some power supplies have a switch to change between 230 V and 115 V. Other models have automatic sensors that switch input voltage automatically, or are able to accept any voltage between those limits. Power supply units used in computers are nearly always switch mode power supplies (SMPS). The SMPS provides regulated direct current power at the several voltages required by the motherboard and accessories such as disk drives and cooling fans.






0 comments:
Post a Comment